The Difference Between Laser Etching Laser Marking and Laser Engraving
Release time:
2025-09-26
Author:
Source:
Explore the distinctions between laser etching, laser engraving, and laser marking. Learn how fiber and CO2 laser marking offer precision for diverse applications.
In the world of laser technology, the terms laser etching, laser marking, and laser engraving are often used interchangeably. However, they are distinct processes with unique applications and outcomes. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses and individuals looking to choose the right laser technique for their needs. In this article, we’ll explore each process, its applications, and how they differ from each other.
Laser technology has revolutionized how we create marks, designs, and patterns on various materials. Whether it's for branding, personalization, or industrial purposes, lasers offer precision and versatility.
What is Laser Etching?
Laser etching is a subset of laser marking. It involves using a high-heat laser beam to melt the surface of a material, creating a raised mark. The process does not remove material but rather causes it to expand. This creates a contrasting, durable mark on the surface.
Applications of Laser Etching
Laser etching is commonly used for items such as:
- Jewelry: Adding names, dates, or designs to metal surfaces.
- Consumer Electronics: Etching logos or serial numbers on devices.
- Medical Devices: Marking critical information on surgical instruments.
What is Laser Marking?
Laser marking covers a variety of processes, including laser etching. It involves altering the surface of a material to create a visible mark. Unlike etching or engraving, laser marking often doesn't involve removing material.
Types of Laser Marking
- Annealing: Commonly used on metals, it heats the surface to create oxidation, resulting in a color change.
- Staining: This method changes the color of the material, typically used on plastics.
- Foaming: Creates gas bubbles in the material, producing a raised mark with a lighter color.
Applications of Laser Marking
Laser marking is versatile and used in many industries:
- Automotive: Marking parts with serial numbers and barcodes.
- Aerospace: Ensuring parts are traceable and compliant with regulations.
- Manufacturing: Branding and labeling products with logos or batch numbers.
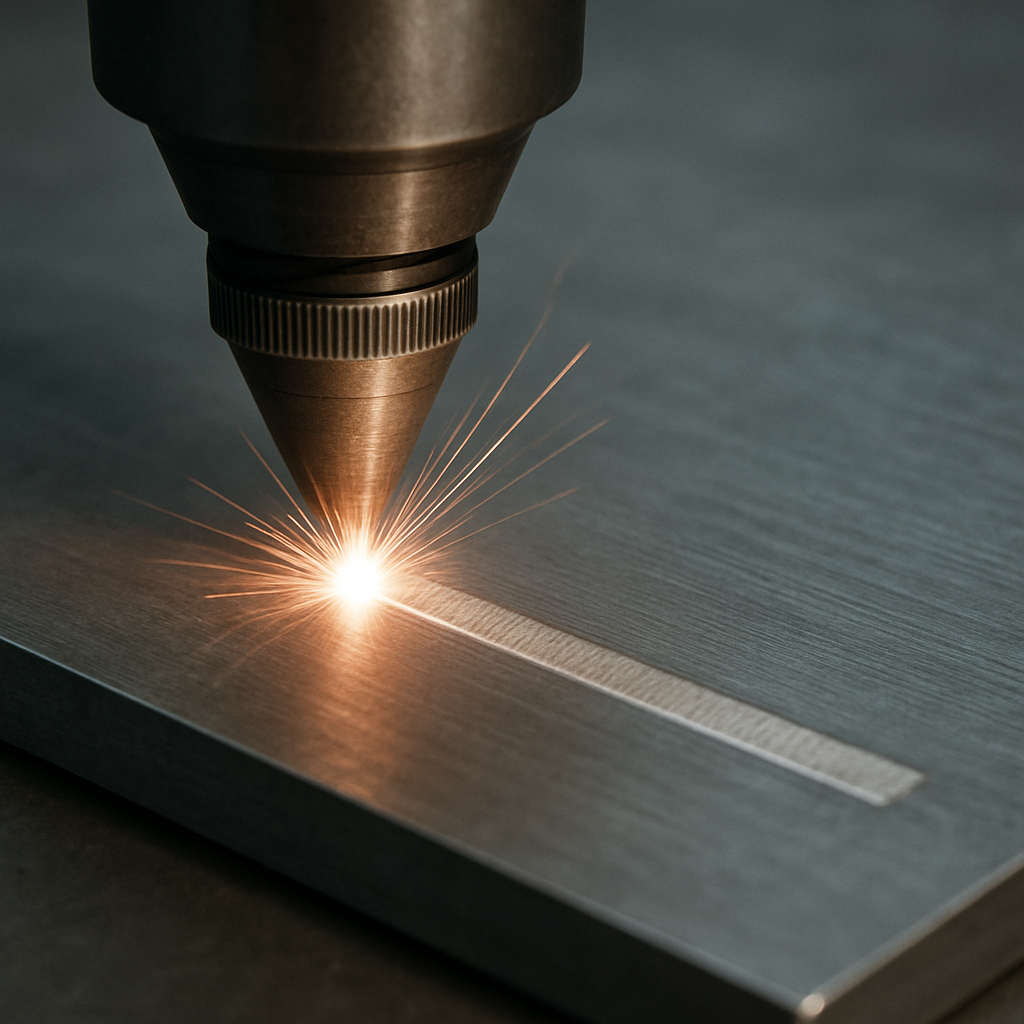

What is Laser Engraving?
Laser engraving involves using a laser to remove material from the surface, creating a cavity that forms the desired image or text. This process is deeper than etching or marking, resulting in a more pronounced effect.
Applications of Laser Engraving
Laser engraving is ideal for:
- Trophies and Awards: Creating detailed and permanent designs.
- Gifts and Personal Items: Customizing items with names or messages.
- Industrial Components: Engraving detailed schematics or text for identification.
Comparing the Techniques
Now that we understand each process, let's compare them based on several factors.
Depth and Durability
- Laser Etching: Creates a shallow mark by melting the surface, offering moderate durability.
- Laser Marking: Alters the surface without depth, resulting in a very durable mark.
- Laser Engraving: Removes material, creating deeper and highly durable marks.
Speed and Cost
- Laser Etching: Generally faster than engraving, making it cost-effective for large volumes.
- Laser Marking: Often the quickest process, especially with fiber laser marking on metals.
- Laser Engraving: Slower due to material removal, potentially increasing costs.
Material Suitability
- Laser Etching: Best for metals and some plastics.
- Laser Marking: Suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics.
- Laser Engraving: Works well on metals, wood, glass, and some plastics.

Choosing the Right Process
When deciding which laser technique to use, consider the following:
- Material Type: Ensure the process is compatible with your material.
- Desired Outcome: Consider the depth, visibility, and durability of the mark.
- Cost and Efficiency: Balance your budget with the production speed required.
- Application Needs: Match the process to your specific industry or personal use needs.
Innovations in Laser Technology
Recent advancements in laser technology have expanded the capabilities and applications of these processes. Fiber laser marking, for example, has become increasingly popular due to its speed and precision, particularly for metal marking.
Fiber Laser Marking
Fiber laser marking uses a laser beam delivered through a fiber optic cable, providing high precision and speed. It's ideal for high-volume production environments and offers excellent results on metals and some plastics.
CO2 Laser Marking
CO2 laser marking is highly effective on non-metal materials, including wood, glass, and acrylic. It's known for its versatility and ability to create clear, crisp marks.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between laser etching, laser marking, and laser engraving is essential for selecting the right process for your project. Each technique offers distinct advantages depending on the material, desired outcome, and application. By considering these factors, you can ensure the best results for your laser marking needs.
Incorporating the latest innovations in laser technology, such as fiber and CO2 laser marking, can further enhance the efficiency and quality of your marking processes. Whether for industrial, commercial, or personal use, these laser techniques continue to offer unmatched precision and versatility.
Key words:
fiber laser marking,laser marking,co2 laser marking,laser engraving,laser etching
Floor 16, Building A, Rongsheng Times International, Licheng District, Jinan City, Shandong Province,China